Robotic knee replacement surgery represents a significant shift in the replacement of joints that can now employ the skills of human surgeons and the accuracy provided by robots. In regular surgery, the instruments used are manual, whereas robots refer to 3D technology that provides precise guidance for submillimeter accuracy. Patients like those from Mumbai can get the benefits provided by advanced institutions regarding the surgery.
Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement Surgery Involves These Steps
All the steps involved in the robotic knee replacement in Mumbai are described below:-
Step 1: Preoperative Assessment and Planning
It includes weeks of evaluation before actual surgery, where surgeons analyze patients’ damaged knees through an X-ray and MRI scan in terms of suitability, which is usually done on patients with severe osteoarthritis of the knees. A critical distinguishing factor is our CT scan, which shows a precise impression of a patient’s knee, creating a model of a 3D nature,” says Patel.
The software replicates bone cuts and implant positions while taking into account ligaments, alignment, and motion. This personalized treatment program, which can be changed before surgery, provides optimal outcomes. Experienced joint replacement surgeons in Mumbai use these simulations to compensate for common errors in surgical procedures that might be prevalent in the Indian body type.
Step 2 – Preparation for Surgery Day
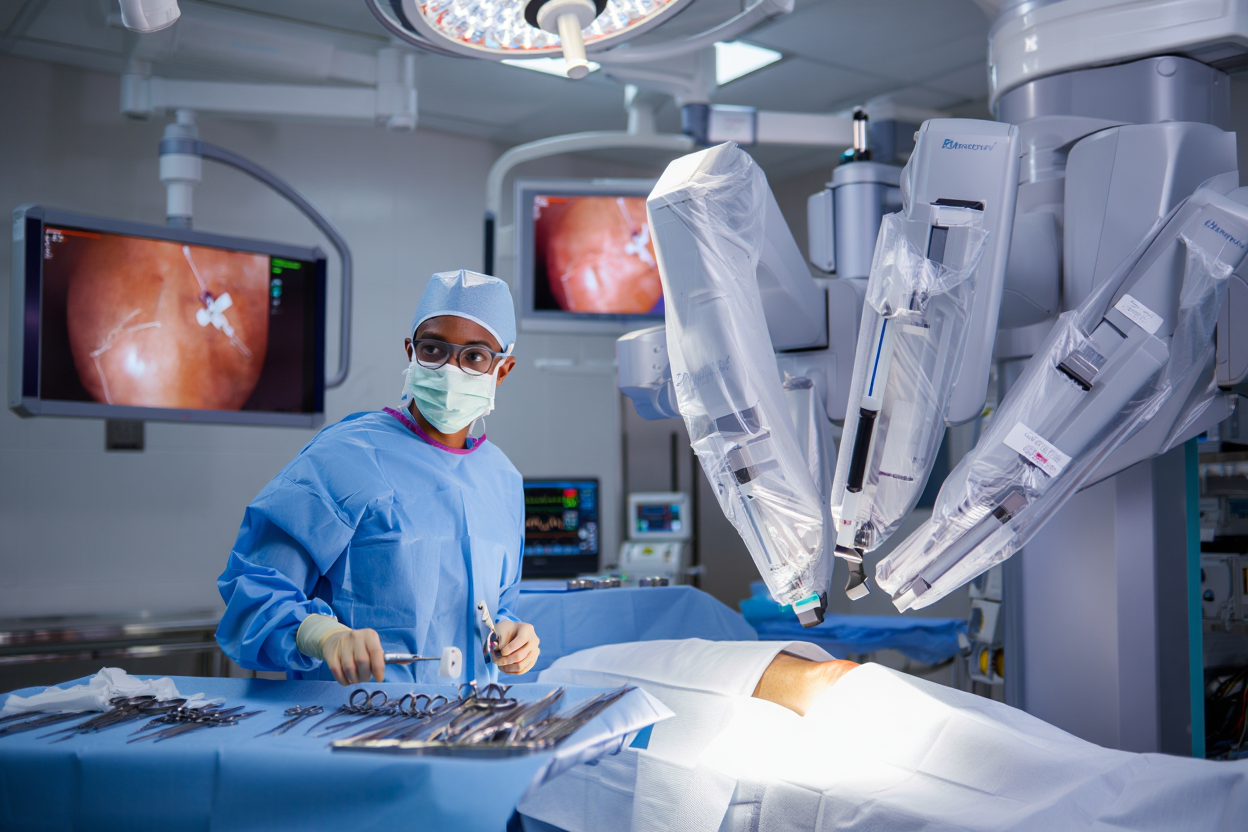
Overnight fasting, preoperative antibiotics. Anesthesia can be spinal or general, providing patient comfort; spinal anesthesia also promotes patient mobilization following surgery. One of the legs undergoing surgery will be sterilized, and it will be possible to use a tourniquet for bleeding control. A robotic system, such as Mak or ROSA, will be positioned in the modulated operating room.
Step 3: Surgical Exposure and Registration
A 6-10 inch incision is required to view the knee joint without dissecting muscles and tendons. Registration of the knee involves attaching optical trackers to the femur and tibia. These trackers relate fundamental physiological aspects to the model used through infrared cameras. Imaging is done in real time to ensure proper positioning for a dynamic map controlled by the surgeon.
Step 4: Robotic Bone Preparation
The robotic arm is an innovation that the surgeon uses with the benefit of tactile sensitivity, having the ‘vibration boundary’ function that prevents the surgeon from over-cutting. From the model, the exact resections to remove the defective cartilage and bone include the femoral condyles in a sequential process, followed by the tibial plateau.
The precise dimensions of the implants are employed in cutting, with consideration of ligament balance, as in the movements of nature. It cannot be done in the standard operating procedure and results in a 30-50% reduction in soft tissue damage.
The elements of a trial are utilized to test how well an implant might fit, how stable it is, or how it moves. The adjusting elements help to adjust a plan dynamically. Mumbai’s robotic knee replacement doctors excel in this area, as their robotic system has the ability to adapt during surgery in cases of obese or deformed knees.
Step 5: Placement of Implant and Verification
Custom-made implants made of metal alloys and/or polyethylene spacers and sometimes cementlessly fixed are used. The robotic system provides accurate positioning of varus and valgus (<1° deviation) and rotation to result in symmetrical wear and tear of the implant. The surgeon checks for this to happen through gap balancing to check for symmetric tension in both flexion positions.
Highly advanced haptic technology prevents the robotic arm from moving beyond the limits in case it tries to do so, and allows control of the arm by the surgeon. Patella resurfacing, if needed, is done with equal.
Step 6: Wound Closure and Immediate Post-Op
Irrigation clears debris; closure in layers is done using absorbable sutures or staples. Drains are applied to prevent hematomas. Patients are turned prone to the recovery room for pain management to be started (multimodal approach including nerve blocks and NSAIDs). Blood loss is decreased by 15% to 20% in robotically assisted surgeries.
Conclusion
Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement Surgery is a combination of 3D surgery, real-time robotic assistance, and execution is done in robotic-assisted replacement surgery of the knee.
The entire surgical process, from preoperative to postoperative implantation, is designed to ensure natural functioning and long-lasting components. Aims and objectives should always include this futuristic technology for a lifetime of freedom. “Feel the Experience of Precision Healing!” Team Orthorobotics today!!!